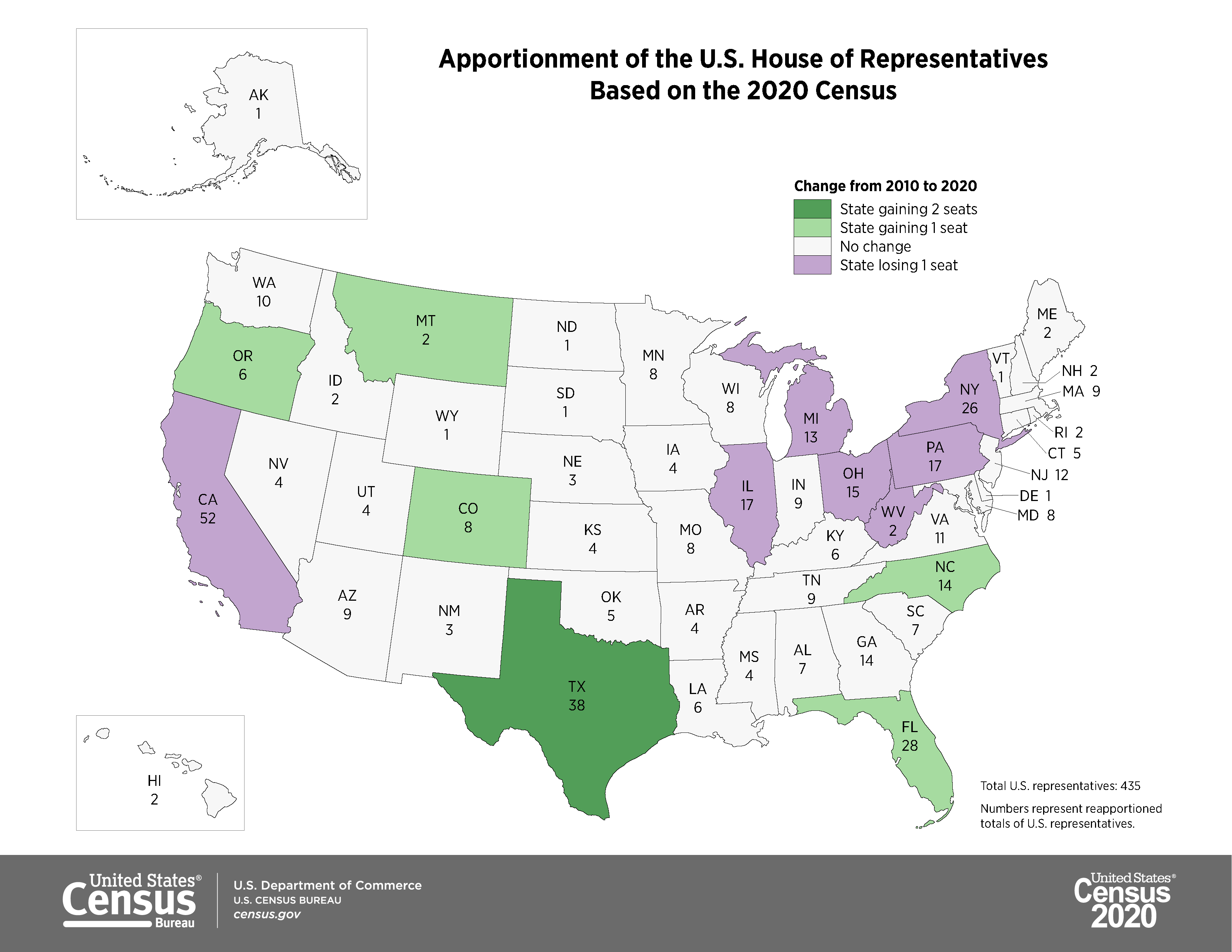
The Great Compromise created Congress’s two-chamber structure during the Constitutional Convention
The Great Compromise of 1787 established a bicameral Congress, balancing population-based representation in the House with equal representation for each state in the Senate—a system designed to reconcile the competing interests of large and small states.